Design of a 48 V three-phase inverter: For automotive applications
Master's thesis in Electric Power Engineering
Fredrik Furst
Department of Energy and Environment
Chalmers University of Technology
Abstract
This project presents a design and construction of a three-phase inverter,
drive circuit and dc-link capacitor bank. The inverter should be able to
supply an electrical machine with 48 V and 250 A. Initial calculations and
simulations were made to get some base for the ordering of hardware. The
inverter board consists of six MOSFETs in parallel for each phase and the
PCB itself is made of aluminum to enable a thermal substrate technique.
The inverter PCBs are mounted on an aluminum frame where liquid runs
between them to cool the inverter. The drive circuit is controlled with a
dSPACE system and the tests are made with a load consisting of cables
and iron powder cores. Temperatures are measured with PT100 sensors
for the water and an infrared camera for the surfaces.
Two di erent MOSFETs were investigated, one with higher switching
losses and one with higher conduction losses. The two inverters were tested
on an RL load and the cooling system picked up around 270 W at a phase
current of 150 Arms. Theoretical calculations, performed with measured
parameters, represents the temperature measurements well. The thermal
resistance between the case and the sink in the inverter, R cs, is measured
to around 0:15 [K=W].
Index Terms: Capacitor bank, cooling system, drive circuit, dSPACE,
inverter, MOSFET, thermal evaluation.
LINK ORIGINAL COMPLETE THESIS
http://publications.lib.chalmers.se/records/fulltext/224623/224623.pdf






















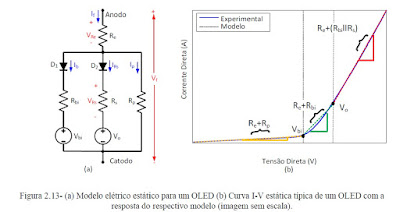

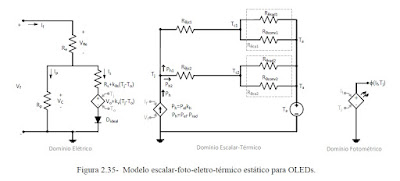
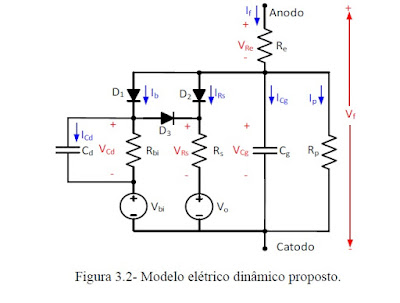








































 JOSIL ARTISTA PLASTICO FORTALEZA CEARA BRASIL AV.HERACLITO GRAÇA 41 TEL(85)32542378
JOSIL ARTISTA PLASTICO FORTALEZA CEARA BRASIL AV.HERACLITO GRAÇA 41 TEL(85)32542378















