Design of a Power Converter for a
Non-starting Air Conditioner Compressor
in Commercial Vehicles
상용차의 무시동시 에어컨 압축기용 전력변환기 설계
Keun-Woo Han
Department of Electrical Engineering
Graduate, School Chonnam National University
(Abstract)
Recently, the direction of automotive technology development is
concentrated on the reduction of the greenhouse gases accelerating global
warming, as well as fuel efficiency improvement against rising oil prices. In
particular, as a means of transportation with high transport efficiency
compared to its vehicle market share, commercial vehicles are playing a key
role in the national logistics industry. In addition, they also play an
important role in all transportation sectors, supporting social overhead
capital including urban construction, roads, bridges, harbors, etc.
Consequently, their annual average mileage is 3.4 times that of passenger
cars, with significant oil consumption or CO2 emission, which increases the
need to develop eco-friendly technologies and increase energy efficiency.
Commercial vehicles, which were recognized as a simple means of
transportation in the past, have also become widely recognized as a second
living space with the addition of space for the driver to sleep . Accordingly,
existing commercial vehicle development is experiencing a change of
direction from performance to the direction in which importance is placed
on safety, comfort and convenience.
The air conditioning system of a vehicle is a core component that
maintains its interior temperature at a comfortable level according to the
preference of passengers, and is of great significance in the aspect of
increased comfort. In general, vehicle air conditioning systems refer to a
unit that maintains a vehicle’s room temperature as desired by its driver
using the energy generated by engine operation (driving or idling). Since the
operation of such air conditioning systems utilize part of the engine’s
driving force, it has s significant relation to the vehicle’s fuel efficiency. In
particular, in the case of commercial vehicles, the utilization rate of an air
conditioning system depends greatly on the driving habits of a driver when
waiting for work during the summer season or when a driver frequently
sleeps in the vehicle at night. Consequently, commercial vehicles which use
air conditioners frequently and for long periods during the summer season
need to have their large engines operating frequently, thereby causing
environmental pollution due to excessive fuel consumption and exhaust gas.
In addition, it is required that new vehicles must meet the Euro III Emission
regulation and be equipped with a control system that automatically stops
the engine when the vehicle remains idling for more than 5 minutes.
Therefore, the problem regarding air conditioning (cooling) of commercial
vehicles, including cargo vehicles and express buses, must be solved.
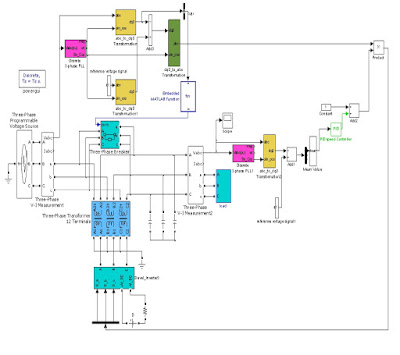
This paper proposes a power converter for a non-starting air conditioner
compressor for commercial vehicles in order to solve the problem of air
conditioning (cooling) of a commercial vehicle when it remains stopped. The
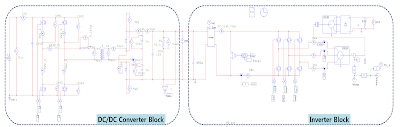
proposed system consists of a DC/DC converter and a 3 phase DC/AC
inverter. In order for the air conditioning system to be operative in the
non-starting state of the vehicle, an electrically driven compressor and 3
phase inverter operated at 200V and higher are required. However, in the
case of a commercial vehicle, it is composed of a 24V battery-based DC
system only. Therefore, in order to supply a non-starting air conditioner
compressor system, a converter that can increase the voltage of the 24V
battery by more than 10 times is indispensible.
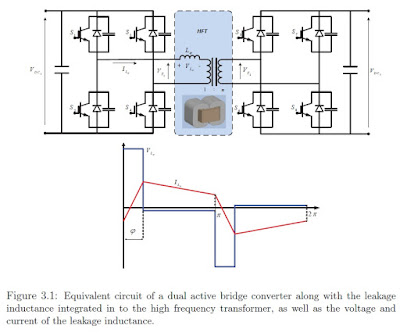
In the case of a converter for a non-starting air conditioner system, it
requires high efficiency and high power density along with low voltage
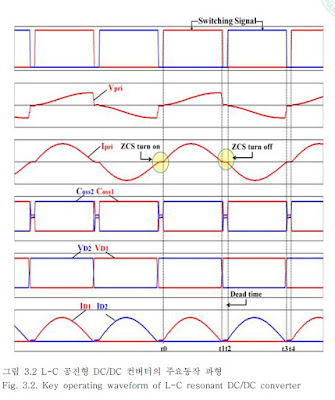
(24V) and high current characteristics. Therefore, a resonant type converter
with an advantage of reduced loss due to high frequency switching is
suitable for a power converter. In order to meet such conditions, this paper
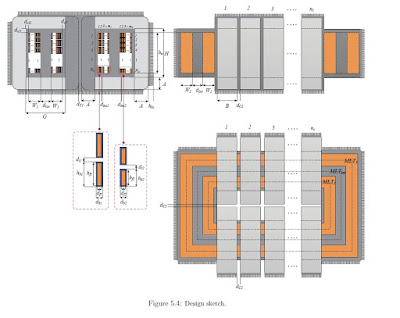
configured a L-C resonant type DC/DC converter with a half-bridge
structure, consisting of a voltage doubler circuit and high frequency
transformer. For the configured converter, the transformer leakage
inductance and capacitor of the voltage doubler circuit are used for
resonance without using an additional resonant tank. This enabled zero
current switching (ZCS) to be available and also allows the converter to be
designed in such a way that the switching loss at the primary side of the
DC/DC converter transformer through which a current higher than 100A
flows. In addition, the entire size and cost of the system were reduced by
replacing the inductance component necessary for the resonant circuit with
the transformer leakage inductance. As a result, unlike vehicles to which an
existing mechanical compressor is applied, it can be seen that fuel
consumption and exhaust gas emissions were reduced because no fuel was
consumed separately during non-starting period.
It is expected that the proposed power converter will ensure high
efficiency under 24V low power supply conditions and be suitable for the
power converter for similar air conditioner compressors for which a low
withstanding voltage inverter module can be used.




























































 JOSIL ARTISTA PLASTICO FORTALEZA CEARA BRASIL AV.HERACLITO GRAÇA 41 TEL(85)32542378
JOSIL ARTISTA PLASTICO FORTALEZA CEARA BRASIL AV.HERACLITO GRAÇA 41 TEL(85)32542378















