domingo, 17 de março de 2019
ANALYSIS AND CONTROL OF GRID-CONNECTED THREE-LEVEL T-TYPE CONVERTERS-Author Payam Alemi Graduate School of Yeungnam University Department of Electrical Engineering
ANALYSIS AND CONTROL OF GRID-CONNECTED THREE-LEVEL T-TYPE CONVERTERS
Ph.D. Thesis Author Payam Alemi
Graduate School of Yeungnam University Department of Electrical Engineering Control and Electric Machinery ∙ Power Conversion Major
Abstract
In this research the brief overview of multilevel converter topologies is presented and the efficiency of multilevel converters is checked by a comparative analysis of power losses for the three-level T-type and neutral-point clamped (NPC) PWM inverters in which the conduction and switching losses of semiconductor devices of the inverters are taken into account. Power losses for the T-type and NPC inverters are analyzed and calculated at the different operating points of MI, PF and the switching frequency, in which the four different models of semiconductor devices are adopted. Then a generalized power loss algorithm for multilevel NPC PWM inverters is proposed to find the power losses in higher levels of NPC inverters, which is applicable to any level number of multilevel inverters. In the case of higher level of inverters than the threelevel, the loss of semiconductor devices cannot be analyzed by conventional methods. The modulation depth should be considered in addition, to find the different conducting devices depending on the MI. In the case of AC/DC/AC PWM converter topology which is widely used in the field of AC motor drives, the DC-link capacitor is the most critical component in determining the life time of the converter which is large, heavy and unreliable. A novel control algorithm that minimizes the DC-link capacitance in the T-type three-level back-to-back converter is proposed. For this, the charging and discharging currents through the capacitor should be minimized, which can be achieved by utilizing the power balance of the AC/DC converter. Then, the voltage variation in the DC-link is also decreased, which makes a significant reduction in the size of DC-link capacitors. With this scheme, the electrolytic capacitors can be replaced by film capacitors which are of higher power density, longer life time and higher reliability. Beside the advantages of PWM converters, there is an issue to mitigate the PWM harmonic ripples in the grid current. To reduce the current harmonics around the switching frequency (2-15 kHz), a relatively large value of input inductance is needed. Due to the disadvantages in terms of inductor size, which can deteriorate the system d ynamics and also the cost of inductors which can be a point in the case of high range, the LLCL filters topology is presented. The LLCL filters structure consists of connecting a small inductor in series with the capacitor in the conventional LCL filters, which can attenuate the switching-frequency-related current ripples more effectively than the LCL filters, resulting in a significant reduction in the grid-side i nductor size. However, the resonance phenomenon is still an issue to solve in this filter. Th e active damping control scheme of LLCL filters based on the PR (proportional-resonant) regulator and virtual resistor methods are proposed to suppress the filter resonance for the grid-connected three-level T-type PWM converter systems. The validity of the power loss analysis has been verified by the Matlab simulation for the three-and five-level NPC inverters and experiment for three-level NPC inverter. The modulation depth needs to be considered for higher level than three-level inverters. In the five-level inverter, the jumps of the conduction and switching power losses occur at MI=0.5 where the modulation depth changes. The PSIM simulation and experimental results have been shown to verify the effectiveness of the proposed strategy for DC-link capacitor minimization where a 3-kW converter system with a 50μF film capacitor operated in a wide range of speed and load and the DC-link voltage is effectively regulated within allowable ranges. The resonance suppression of LLCL filters in T-type three-level PWM converter has been investigated by PR and virtual resistor active damping methods. In the LLCL filters, the grid-side inductor has been reduced by 60% compared with the LCL filters from 0.8 mH to 0.35 mH in the simulation and from 1 mH to 0.4 mH in the experiment with which the THD and dominant harmonic component of the grid current have met the IEEE standard.
LINK
http://www.mediafire.com/file/3xs2s32qs85fc3f/ANALYSIS_AND_CONTROL_OF_GRID_CONNECTED_THREE_LEVEL_T-TYPE_CONVERTERS.pdf/file
quarta-feira, 6 de março de 2019
Modelling and Characterisation of Losses in Nanocrystalline Cores By Yiren Wang School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering-University of Manchester
School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
University of Manchester
ABSTRACT
The University of Manchester Yiren Wang A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Modelling and Characterisation of Losses in Nanocrystalline Cores September 2015 Increasing the power density of the DC-DC converters requires the size and weight of the magnetic components, such as inductors and transformers, to be reduced. In this thesis, the losses in nanocrystalline inductor cores are characterised and analysed, including the traditional core loss and the gap loss caused by the air gap fringing flux. The loss calculations will form a basis for the design and optimisation of high power inductors for DC-DC converters for EV applications. This thesis first characterises experimentally the core losses in four nanocrystalline cores over a range of operating conditions that are representative of those encontered in typical high power converter applications, including non-sinusoidal waveforms and DC bias conditions. The core losses are assessed by the measured B-H loops and are characterised as a function of DC flux density, showing that for a fixed AC induction level, the losses can vary by almost an order of magnitude as the DC bias increases and the duty ratio moves away from 0.5. The results provide a more complete picture of the core loss variations with both DC and AC magnetisations than is available in manufactures’ data sheets. An electromagnetic finite element (FE) model is used to examine the gap loss that occurs in finely laminated nanocrystalline cores under high frequency operation. The loss is significant in the design example, contributing to almost half of the total inductor loss, and the gap loss is highly concentrated in the region of the air gap. The dependence of the gap loss on key inductor design parameters and operating condtions is also explored. An empirical equation is derived to provide a design-oriented basis for estimating gap losses. Thermal finite element analysis is used to estimate the temperature rise and identify the hot spot in a nanocrystalline inductor encapsulated in an alumimium case. The temperature distribution in the core largely corresponds to the non-uniform distribution of the gap loss. The thermal FEA can also be used to evaluate different thermal management methods to optimise the design for a more compact component. The FE modelling of gap loss and the thermal predictions are validated experimentally on a foil-wound Finemet inductor, showing good agreement between the predictions and measurements under various operating conditions.
LINK
https://www.research.manchester.ac.uk/portal/files/54578747/FULL_TEXT.PDF
domingo, 3 de março de 2019
Dc Line-Interactive Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) with Load Leveling for Constant Power and Pulse Loads Seyed Ahmad Hamidi University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
DC LINE-INTERACTIVE UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS) WITH LOAD LEVELING FOR CONSTANT POWER AND PULSE LOADS by Seyed Ahmad Hamidi
A Dissertation Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophyin Engineering at The University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee May 2017
ABSTRACT
DC LINE-INTERACTIVE UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS) WITH LOAD LEVELING FOR CONSTANT POWER AND PULSE LOADS by Seyed Ahmad Hamidi The University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, 2017
Under the Supervision of Professor Dr. Adel Nasiri
Uninterruptable Power Supply (UPS) systems are usually considered as a backup power for electrical systems, providing emergency power when the main power source fails. UPS systems ensure an uninterruptible, reliable and high quality electrical power for systems with critical loads in which a continuous and reliable power supply is a vital requirement. A novel UPS system topology, DC line-interactive UPS, has been introduced. The new proposed UPS system is based on the DC concept where the power flow in the system has DC characteristic. The new DC UPS system has several advantageous with respect to the on-line 3-phase UPS which is extensively used in industry, such as lower size, cost and weight due to replacing the three-phase dual converter in the on-line UPS system with a single stage single phase DC/DC converter and thus higher efficiency is expected. The proposed system will also provide load leveling feature for the main AC/DC rectifier which has not been offered by conventional AC UPS systems. It applies load power smoothing to reduce the rating of the incoming AC line and consequently reduce the installation cost and time. Moreover, the new UPS technology improves the medical imaging system up-time, reliability, efficiency, and cost, and is applicable to several imaging modalities such as CT, MR and X-ray as well. A comprehensive investigation on different energy storage systems was conducted and couple of most promising Li-ion cell chemistries, LFP and NCA types, were chosen for further aggressive tests. A battery pack based on the LFP cells with monitoring system was developed to be used with the DC UPS testbed. The performance of the DC UPS has also been investigated. The mathematical models of the system are extracted while loaded with constant power load (CPL) and constant voltage load (CVL) during all four modes of operation. Transfer functions of required outputs versus inputs were extracted and their related stability region based on the Routh-Hurwitz stability criteria were found. The AC/DC rectifier was controlled independently due to the system configuration. Two different control techniques were proposed to control the DC/DC converter. A linear dualloop control (DLC) scheme and a nonlinear robust control, a constant frequency sliding mode control (CFSMC) were investigated. The DLC performance was convincing, however the controller has a limited stability region due to the linearization process and negative incremental impedance characteristics of the CPL which challenges the stability of the system. A constant switching frequency SMC was also developed based on the DC UPS system and the performance of the system were presented during different operational modes. Transients during mode transfers were simulated and results were depicted. The controller performances met the control goals of the system. The voltage drop during mode transitions, was less than 2% of the rated output voltage. Finally, the experimental results were presented. The high current discharge tests on each selected Li-ion cell were performed and results presented. A testbed was developed to verify the DC UPS system concept. The test results were presented and verified the proposed concept.
LINK ORIGINAL
https://dc.uwm.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=2486&context=etd
sábado, 2 de março de 2019
Design of UPS with Customer Load Management Function Ko, Jae Hun School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Graduate School of Chungbuk National University-2019
Design of UPS with Customer Load Management Function Ko, Jae Hun
School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science,
Graduate School of Chungbuk National University Cheongju, Korea
Supervised by Professor Kim, Jae Eon
Abstract
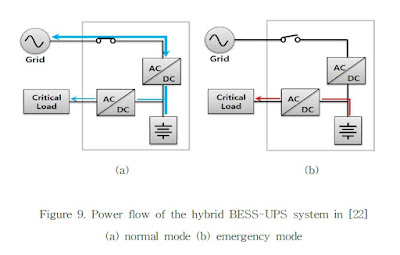
Traditional Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) only provide stable power to critical loads in emergency situations, while Energy Storage Systems (ESS) perform functions such as generator output stabilization, frequency control, peak shaving, and load leveling. As the global ESS market expands, various ESS supply policies are being implemented in a number of countries. Accordingly, research and development of a hybrid BESS-UPS system combining the advantages of UPS and BESS are underway in order to ensure critical load stability in case of emergency. For such a situation, we propose the development of a system with a customer load management function by simply adding a converter and battery pack to a widely used conventional UPS. The proposed system in this paper is more economical than a hybrid BESS-UPS system or an BESS. In addition, the proposed system performs load-shifting according to time-based rates, and has a longer power outage time in case of emergency without needing to communicate with the existing UPS.
Assinar:
Postagens (Atom)









































































 JOSIL ARTISTA PLASTICO FORTALEZA CEARA BRASIL AV.HERACLITO GRAÇA 41 TEL(85)32542378
JOSIL ARTISTA PLASTICO FORTALEZA CEARA BRASIL AV.HERACLITO GRAÇA 41 TEL(85)32542378















