domingo, 30 de agosto de 2020
Design and implementation of a GaN based dual active bridge converter for electric vehicle charger-CANDIDATE: Marco Giacomazzo-INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Master’s degree in Electrical Energy Engineering-University of Padua
sexta-feira, 28 de agosto de 2020
A Study on the Efficiency Improvement of Inverter for Automotive using SiC MOSFET SiC MOSFET를 이용한 차량용 INVERTER 효율 향상에 관한 연구--KOREA NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF TRANSPORTATION
A Study on the Efficiency Improvement of Inverter for Automotive using SiC MOSFET
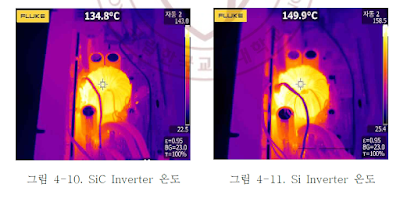
In this paper, we measured the loss of conduction, switching loss, efficiency characteristics, and the temperature of the main parts for Si / SiC MOSFET. In the conduction loss experiment, the loss value of SiC MOSFET compared to Si MOSFET for one cycle is approximately 61.3(%). The switching loss experiment showed that SiC MOSFET losses were small, with about 49.6(%) at Turn-on and approximately 49.2(%) at Turn-off against Si MOSFET. This was immediately confirmed to be low temperature in each part of the inverter. In particular, it was found that the temperature difference at the transformer core with the highest temperature varies from the load of 600(W) to 15.1(°C). In the experiment of efficiency characteristics, the maximum efficiency of 93.5(%) was obtained, and the efficiency improvement of up to 2.8(%) compared to the inverter with Si MOSFET was achieved. The temperature measurement test also shows that most parts temperature is low in the inverter employing SiC MOSFET. The application of SiC MOSFET to the efficiency of inverter was proved to be reasonable as the performance of inverter with SiC
quarta-feira, 19 de agosto de 2020
공동주택에 적용한 계통연계형 태양광발전시스템의 보호방식에 관한 연구 A Study on the Protection Method of the Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Power Generation System Applied to Apartments-GeunYub Lee- Dept. of Electrical Eng. The Graduate School Korea University
MANUAL DE ENGENHARIA PARA SISTEMAS FOTOVOLTAICOS-JOÃO TAVARES PINTO-MARCO ANTONIO GALDINO-GRUPO DE TRABALHO DE ENERGIA SOLAR-GTES-CEPEL-DTE-CRESESB
MANUAL DE ENGENHARIA PARA SISTEMAS FOTOVOLTAICOS-JOÃO TAVARES PINTO-MARCO ANTONIO GALDINO-GRUPO DE TRABALHO DE ENERGIA SOLAR-GTES-CEPEL-DTE-CRESESB
segunda-feira, 17 de agosto de 2020
Control Architecture for Parallel Inverter in Uninterruptible Power Systems Chi Zhang, Student Member, IEEE, Josep M. Guerrero, Fellow, IEEE, Juan C. Vasquez, Senior Member, IEEE, Ernane A.A. Coelho, Member, IEEE
Abstract— In this paper, a control strategy for the parallel operation of three-phase inverters forming an online uninterruptible power system (UPS) is presented. The UPS system consists of a cluster of paralleled inverters with LC filters directly connected to an AC critical bus and an AC/DC forming a DC bus. The proposed control scheme comprises two layers: (i) a local layer that contains a “reactive power-to-phase droop” in order to synchronize the phase angle of each inverter and a virtual resistance loop that guarantees equal power sharing among inverters; and (ii) a central controller that guarantees synchronization with an external real/fictitious utility, and critical bus voltage amplitude restoration. Improved transient and steady-state frequency, active, reactive and harmonic power sharing, and global phase-locked loop resynchronization capability are achieved. Detailed system topology and control architecture are presented in this paper. Further, a mathematical model was derived in order to analyze critical parameters effects on system stability. The proposed control approach has been validated by means of experimental results obtained for several case-study scenarios. Index Terms— UPS system; parallel inverters; voltage restoration; droop control; virtual impedance
domingo, 16 de agosto de 2020
Updating and Customizing an industrial UPS HMI-A Master's Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of the Escola Tècnica d'Enginyeria de Telecomunicació de Barcelona Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya by Ali Ahmadi
quinta-feira, 13 de agosto de 2020
Optimal Design Method of the LLC resonant converter using the hybrid current balancing circuit for LED lighting -Author Jin-Gu Kim Department of Electrical & Medical Convergent Engineering Graduate School, Kangwon National University South Korea.
Optimal Design Method of the LLC resonant converter using the hybrid current balancing circuit for LED lighting Author Jin-Gu Kim
Department of Electrical & Medical Convergent Engineering Graduate School, Kangwon National University South Korea.
Abstract
In this thesis, a novel hybrid current balancing circuit and an optimum design of LLC resonant converter for driving a current balancing circuit are proposed.
First of all, the hybrid current balancing circuit was proposed for compensating current deviation among LED strings. LEDs have been widely used in lighting, automobiles, and airplanes owing to their excellent light output characteristics and long lifespan. Though LEDs are manufactured under the same process, variations in impurity concentrations cause electrical deviation among LEDs. This electrical deviation results in current unbalance of LED strings. The resulting current unbalance does not only reduce the life time of the LED but also cause non-uniform luminance of LEDs connected in parallel. The LED driving circuit is researched to solve the above problems. In this thesis, a novel hybrid current balancing circuit with a Y-type current balancing transformer and a voltage doubler rectifier circuit was proposed for the compensation of 6 LED strings with a simple structure.
Secondly, the Optimal design method of LLC resonant converter for driving hybrid current balancing circuit was proposed. The difference between the proposed optimal design method of LLC resonant converter and conventional design method can be divided into three categories.
First of all, when designing transformer with leakage inductance(Lr ) and magnetizing inductance(Lm), unwanted leakage inductance of secondary side (Lr2) which cause error in the process of measuring the leakage inductance (Lr ) with instrument occurs. This design error could be reduced by taking into account the leakage inductance of secondary side(Lr2).
Secondly, in general, the voltage gain characteristic curve is applied to design LLC resonant converter. in this thesis, the current gain characteristic curve was applied to the design process which is suitable for LED that is non-linear load and necessary to be controlled to a constant current.
Lastly, the equivalent circuit of LED was applied to the design process. Normally, a resistive load which has linear load characteristic is used for designing the LLC resonant converter. However, in this thesis, the equivalent circuit of LED which includes a voltage source, a resistor and a diode could be obtained by using the linear approximation method. This circuit was then applied to the design process for reducing design error.
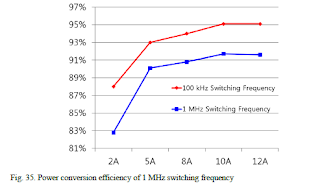
Experimental results are presented to verify the performance of the proposed hybrid current balancing circuit and the optimal design method of the LLC resonant converter. The LED maximum current error rate which was 19.57% was reduced to 4.5% by Y-type current balancing transformer. Also, the validity of the proposed optimal design method of the LLC resonant converter was verified by comparing it with the conventional design method. An 150W prototype was implemented and used for the performance verification of the hybrid current balancing circuit and the LLC resonant converter.
terça-feira, 11 de agosto de 2020
Master's Thesis Design, Control, and Implementation of High Frequency LLC Resonant Converter-Author- Hwa-Pyeong Park Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering -ULSANG NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Master's Thesis
sábado, 8 de agosto de 2020
Méthodologie de conception numérique d’un module de puissance dédié à l’automobile en vue de l’optimisation des surtensions, des pertes et des émissions conduites Hocine Dao--Thèse de doctorat de l'Université Paris-Saclay préparée à L’École Normale Supérieure de Cachan (École normale supérieure Paris-Saclay)-
Vieillissement accéléré de modules de puissance de type MOSFET SiC et IGBT Si basé sur l'analyse de profils de mission d'onduleurs photovoltaïques. Mouhannad Dbeiss--Institut Polytechnique de Grenoble
quinta-feira, 6 de agosto de 2020
Elaboration sans prototypage du circuit équivalent de transformateurs de type planar-Présentée et soutenue publiquement par Xavier MARGUERON-THESE Pour obtenir le grade de DOCTEUR DE L’UNIVERSITE JOSEPH FOURIER
quarta-feira, 5 de agosto de 2020
CARREGADOR DE BATERIAS MONOFÁSICO PARA APLICAÇÃO EM VEÍCULOS ELÉTRICOS -Autor César Orellana Lafuente - CENTRO DE TECNOLOGIA PÓS-GRADUAÇÃO EM ENGENHARIA ELÉTRICA UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE CEARÁ
CARREGADOR DE BATERIAS MONOFÁSICO PARA APLICAÇÃO EM VEÍCULOS ELÉTRICOS









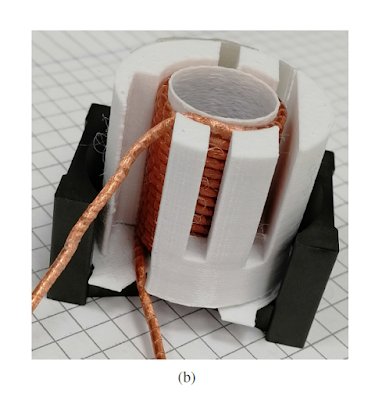

































































 JOSIL ARTISTA PLASTICO FORTALEZA CEARA BRASIL AV.HERACLITO GRAÇA 41 TEL(85)32542378
JOSIL ARTISTA PLASTICO FORTALEZA CEARA BRASIL AV.HERACLITO GRAÇA 41 TEL(85)32542378















