Impact of EV Charging Station on the Electric Distribution Grid
Thesis Supervisor: Morris Brenna
Department of Energy
Politecnico di Milano
Master thesis of:
Dwaramakki Gaurav
Harinarayanan Manimaran
POLITECNICO DI MILANO
School of Industrial and Information Engineering
Master of Science in Electrical Engineering
ABSTRACT
Over the past few years, Electric vehicles have become a very important part of the automotive industry as we try to look for a future less dependent on fossil fuels. A lot of research and development has taken place in this field to improve the existing technology and to develop efficient ones. This continued emphasis on research and development has resulted in great improvements in the technology of Electric vehicles.
In this thesis, we discuss about the features of Electric Vehicles, the existing protocols to charge the battery systems, the battery management system (BMS), the different standards used in various parts of the world and about the infrastructure that is needed to charge the Electric Vehicles and about the different modes of charging.
In the next part of the thesis, we have focussed on the Electric Vehicle and its relationship with the Electric Distribution Grid. Aspects related to PHEV characteristics, Load growth, PHEV Penetration level are looked into. The essence of this thesis is to learn about the Impact of the EV Charging Station on the Electric Distribution Grid. Research papers regarding the impact study of EV Charging station on the Milan Electric Distribution network is considered and discussed.
Finally, we look at the Optimisation of EV charging stations which helps in the overall efficiency of the charging process and lessens its impact on the Electric Distribution Grid. In this study we discuss about various control strategies of battery management, charging and the control of
inverters.
1. INTRODUCTION
The high energy usage, environmental pollution and rising fossil fuel prices, current dependent on Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) technology must be reduced and alternative fuel which has the potential to solve environmental pollution; global warming and energy sustainability concerns must be explored. Taken consideration that electricity is the most suitable energy for transportation in the next 30 years when considering risk, emissions, availability, maintainability, efficiency and reliability [1]. The invention of automobiles with ICE began in the late 19th century and the automotive industry ever since has seen only incremental changes. ICE remains the prime mover for automobiles with fossil fuel as the main fuel.
With the increasing concerns over depletion of natural resources (e.g. oil and gas) and air pollution, governments, automakers and consumers worldwide have been working together to adapt a shift to green transportation. This has spurred intense competition and ongoing revolution in the development of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are an alternative to the internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles with better efficiency and lower CO2 emissions. Among all EVs and HEVs, electrochemical batteries are core components used for energy storage, similar to the fuel tank in ICE vehicles.
Nowadays, EVs represent an interesting solution for the growing dependence from fossil fuels, since they allow a considerable reduction of air pollution. However, the diffusion of EVs is still affected by many issues, which are mainly due to interaction and integration of these types of vehicles with the existing power grid. Moreover, in order to have a wide diffusion on the market of no polluting vehicles, they have to present the characteristics of travel ranges and recharging times comparable to the traditional oil-based fuel vehicles. For these reasons EVs require battery packs characterized by high values of both energy storage capacity and charging rates. From this point of view lithium based batteries represent a very interesting solution, as they are showing a great potential, in recent years, to supply electric vehicles having good performance in terms of acceleration and driving range. Nowadays, new technologies of lithium compounds are available, which permit reaching an specific energy up to 180 Wh/kg and a maximum charging rate of 6 C reducing the charging times up to 10 minutes.
Typically, the charging modes at low power are suitable for charging the battery packs during night time of 7-8 hours, ensuring low power requirements for the grid. In fact, recent studies demonstrate that the daily travel range is less than 50 km in 80% of the cases. For this reason such slow recharging would be acceptable for most users ensuring a travel range from 100 to 150 km during the daylight.
LINK FULL THESIS
https://www.politesi.polimi.it/bitstream/10589/120624/1/Thesis_LM.pdf


























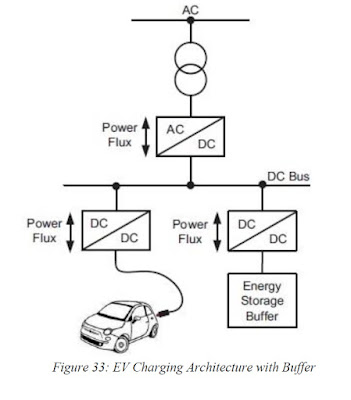




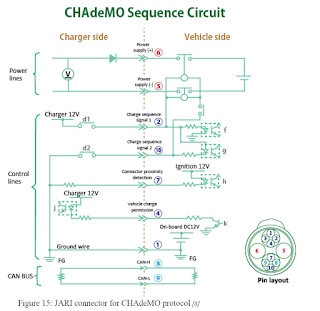
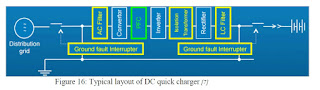


























 JOSIL ARTISTA PLASTICO FORTALEZA CEARA BRASIL AV.HERACLITO GRAÇA 41 TEL(85)32542378
JOSIL ARTISTA PLASTICO FORTALEZA CEARA BRASIL AV.HERACLITO GRAÇA 41 TEL(85)32542378
















